Prescription Anxiety Relief
Relief that's non-sedating, non-addictive, and safe for long-term use.
Clear the FogRx Available by prescription only


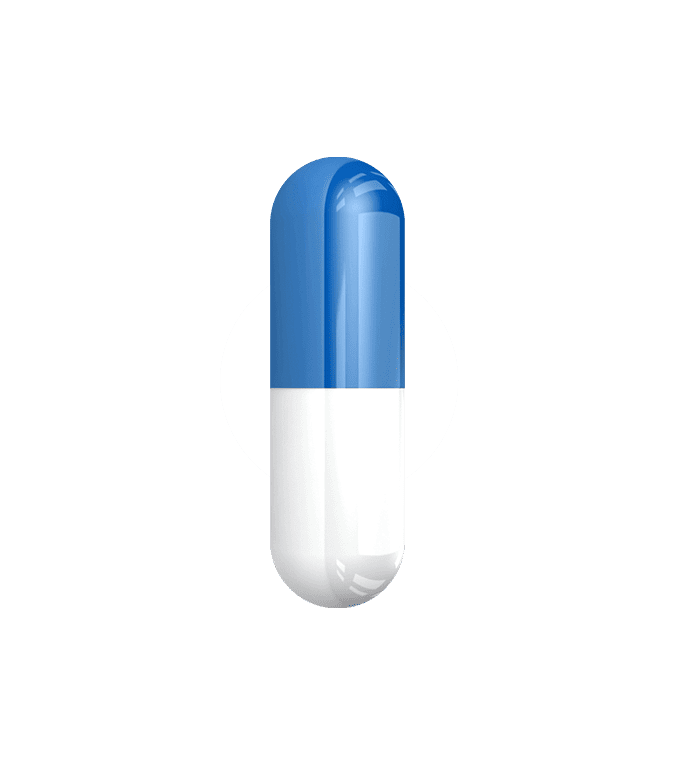
Bucapsol™ (buspirone hydrochloride) capsules are a new-generation anxiety relief option that's accessible, non-sedating, and non-addictive. Delivered in smooth, easy-to-swallow capsules for faster relief and on-demand mental clarity.
Non-Sedating
Maintains alertness and cognitive function ‐ no drowsiness or mental fog
Non-Habit-Forming
Not associated with risk of dependence, withdrawal, or abuse
Long-Term Use
Demonstrated safety & tolerability over extended treatment duration
Flexible Dosing
Various capsule strengths supports personalized titration
Why Bucapsol™?
Helps ease chronic feelings of worry, tension, and fear, supporting your return to a more peaceful and productive life.
Indicated for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), Bucapsol™ delivers consistent relief without thesedative effects of benzodiazepines.
Whether it’s daily stress or persistent anxious thoughts, Bucapsol™ targets anxiety symptoms at the source, improving day-to-day functioning.
Bucapsol™ supports mental clarity and calm by gently regulating serotonin activity — no fogginess, just forward momentum.
Unlike many traditional anti-anxiety drugs, Bucapsol™ is non-sedating and non-habit-forming, making it a safe option for long-term anxiety management.

Prescribing Bucapsol™
Bucapsol™ is easy to prescribe and provides considerable patient savings to eligible commercially insured patients
Most eligible commercial patients may pay as little as $0* for Bucapsol™
The Bucapsol™ Savings Program offers most eligible commercially insured patients $0* out of pocket cost on a monthly supply.
No patient registration is required to use the card
The savings card can be applied to initial prescriptions, refills, and 30 or 90-day prescriptions

Additional Medical Information; Rx only
Important Warning
The administration of Bucapsol™ capsules to a patient taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) may pose a hazard. There have been reports of the occurrence of elevated blood pressure when buspirone hydrochloride has been added to a regimen including an MAOI. Therefore, it is recommended that Bucapsol™ capsules not be used concomitantly with an MAOI.
Indications & Usage
Bucapsol™ are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, and Important Safety Information on the product itself.
Individual patient results may vary. To report suspected adverse reactions, contact the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. You may also contact Pangea Pharmaceuticals at 855-892-8224 or drugsafety@pangeapharm.com.
How Supplied
Bucapsol™ capsules are supplied as capsules for oral administration. Bucapsol™ capsules contains 7.5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg of buspirone hydrochloride, USP (equivalent to 6.8 mg, 9.1 mg, and 13.7 mg of buspirone free base, respectively) in a hard gelatin shell. Each capsule also contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium starch glycolate. The shell consists of black ink, gelatin, titanium dioxide, fd&c blue no. 1 (7.5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg), and black iron oxide (10 mg) and is imprinted with edible ink, NDCs 81279-122-60, 81279-123-60, and 81279-124-60 respectively.
Contraindications
Bucapsol™ capsules are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to buspirone hydrochloride.
The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat depression with buspirone or within 14 days of stopping treatment with buspirone is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome and/or elevated blood pressure. The use of buspirone within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat depression is also contraindicated. Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome.
Warnings & Precautions
-
Serotonin Syndrome
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs, SSRIs, and other serotonergic drugs, including buspirone, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans), with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, including reversible MAOIs such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists.
If concomitant use of buspirone with a 5-hydroxytryptmine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of buspirone with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with buspirone and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Because Bucapsol™ capsules has no established antipsychotic activity, it should not be employed in lieu of appropriate antipsychotic treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Cardiovascular Vasoconstrictive complications of a serious nature may occur at times. These include ischemia, cyanosis, absence of pulse, cold extremities, gangrene, precordial distress and pain, EKG changes and muscle pains. Although these effects occur most commonly with long-term therapy at relatively high doses, they have also been reported with short-term or normal doses. Other cardiovascular adverse effects include transient tachycardia or bradycardia and hypertension.
Commonly Observed: The more commonly observed untoward events associated with the use of buspirone hydrochloride not seen at an equivalent incidence among placebo-treated patients include dizziness, nausea, headache, nervousness, lightheadedness, and excitement.
Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment: One guide to the relative clinical importance of adverse events associated with buspirone hydrochloride is provided by the frequency with which they caused drug discontinuation during clinical testing. (See PRECAUTIONS for full clinical testing info)
Cardiovascular: Frequent was nonspecific chest pain; infrequent were syncope, hypotension, and hypertension; rare were cerebrovascular accident, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and bradycardia.
For complete prescribing and dosage information click here


